Applications and standards for galvanized steel pipes
Hot-dip galvanized steel pipes are widely used in construction, machinery, coal mines, chemical industry, electric power, railway vehicles, automobile industry, highways, bridges, containers, sports facilities, agricultural machinery, petroleum machinery, prospecting machinery, greenhouse construction and other manufacturing industries.
Galvanized steel pipesare welded Steel Pipes with hot-dip or electro-galvanized layers on the surface. Galvanizing can increase the corrosion resistance of steel pipes and prolong their service life.Galvanized pipesare widely used, in addition to being used as Line Pipes for water, gas, oil and other general low-pressure fluids, they are also used as oil well pipes and oil pipelines in the petroleum industry, especially in offshore oil fields, oil heaters, condensate coolers, coal distillation and oil exchangers for chemical coking equipment, as well as trestle pipe piles, and pipes for support frames of mine tunnels.
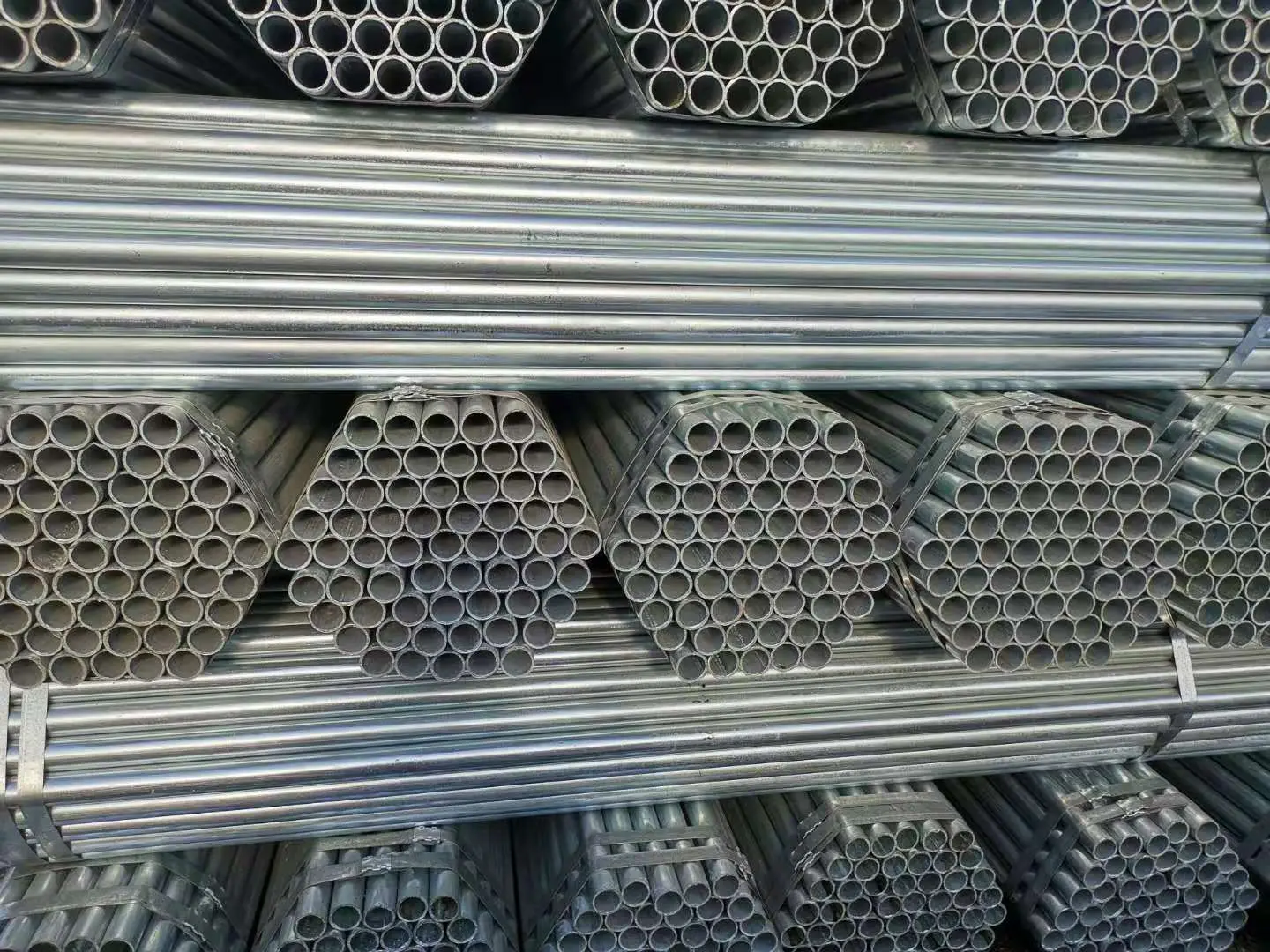

Hot-dip galvanized pipe
Hot-dip galvanized pipe is to react molten metal with iron matrix to produce an alloy layer, so that the matrix and the coating are combined. Hot-dip galvanizing is to pickle the steel pipe first, in order to remove the iron oxide on the surface of the steel pipe, after pickling, it is cleaned in an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride or zinc chloride or an aqueous solution mixed with ammonium chloride and zinc chloride, and then sent to the hot-dip plating tank. Hot-dip galvanizing has the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion and long service life. The hot-dip galvanized steel pipe matrix undergoes complex physical and chemical reactions with the molten plating solution to form a corrosion-resistant and compact zinc-iron alloy layer. The alloy layer is integrated with the pure zinc layer and the steel pipe matrix, so it has strong corrosion resistance.
Cold galvanized pipe
Cold galvanized pipe is electro-galvanized, the amount of galvanization is very small, only 10-50g/m2, and its corrosion resistance is much different from that of hot-dip galvanized pipe. In order to ensure the quality, most of the regular galvanized pipe manufacturers do not use electrogalvanizing (cold plating). Only those small enterprises with small scale and outdated equipment use electrogalvanizing, and of course their prices are relatively cheaper. The Ministry of Construction has officially eliminated the cold galvanized pipes with backward technology, and is not allowed to use cold galvanized pipes for water and gas pipes. The galvanized layer of cold galvanized steel pipe is an electroplating layer, and the zinc layer is independently layered with the steel pipe matrix. The zinc layer is thin, and the zinc layer is simply attached to the steel pipe matrix and is easy to fall off. Therefore, its corrosion resistance is poor. In newly built homes, it is forbidden to use cold galvanized steel pipes as water supply pipes.
Weight factor
Nominal wall thickness (mm): 2.0, 2.5, 2.8, 3.2, 3.5, 3.8, 4.0, 4.5.
Coefficient parameters (c): 1.064, 1.051, 1.045, 1.040, 1.036, 1.034, 1.032, 1.028.
Note: The mechanical properties of steel are an important index to ensure the final use performance (mechanical properties) of steel, which depends on the chemical composition of the steel and the heat treatment regime. In the steel pipe standard, according to different use requirements, the tensile properties (tensile strength, yield strength or yield point, elongation) and hardness, toughness indexes, as well as the high and low temperature properties required by users are specified.
Steel grade: Q215A; Q215B; Q235A; Q235B
Test pressure value/Mpa: D10.2-168.3mm is 3Mpa, D177.8-323.9mm is 5Mpa
Email:manager@fsdsteel.com
Phone/Whatsapp:+86-18831507725