Global Standards and Applications of H-Beams: Diverse Specifications Support High-Quality Construction Projects
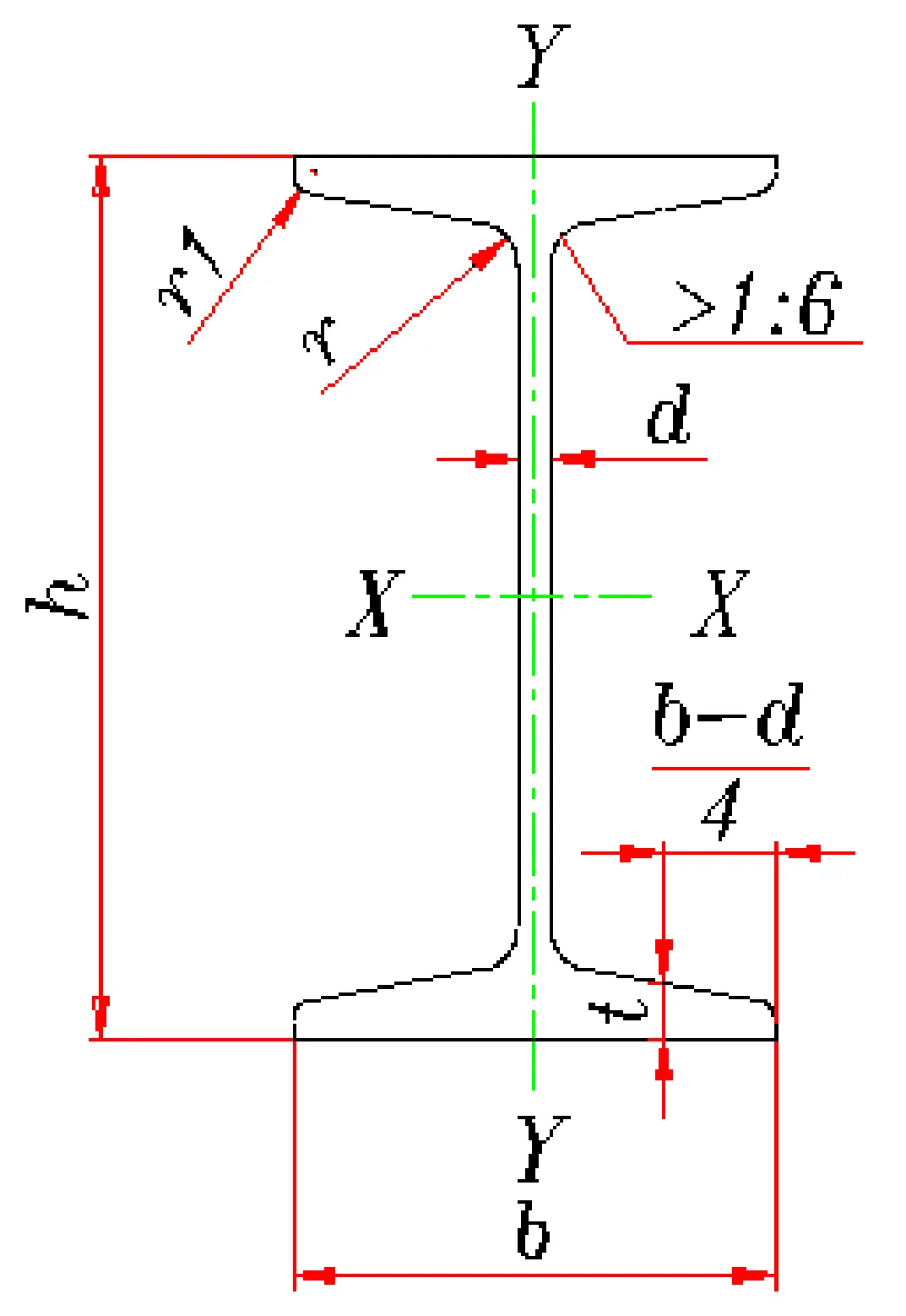
H-beams, a type of Long Steel with an H-shaped cross-section resembling the English letter "H," are widely used in construction, bridges, machinery manufacturing, and other fields due to their high strength and excellent mechanical properties. Different countries have established various H-beam standards to meet the diverse needs of global engineering projects.


Chinese National Standard (GB): Clear Classification, Broad Applications
In China, H-beams are primarily produced in accordance with Hot Rolled H-Beams and T-Beams (GB/T 11263-2017). Based on flange width, they are categorized into wide-flange (HW), medium-flange (HM), and narrow-flange (HN) types. For example, HW100×100 denotes a wide-flange H-beam with a flange width and height of 100 mm, while HM200×150 represents a medium-flange H-beam with a 200 mm flange width and 150 mm height. Additionally, China produces cold-formed thin-walled steel and other specialized H-beams to meet various engineering requirements.
European Standards (EN): Comprehensive Series, Strong Adaptability
European H-beams comply with standards such as EN 10034 and EN 10025, which specify dimensions, material properties, and surface quality. Common series include HEA, HEB, and HEM, each with distinct characteristics:
-
HEA Series (e.g., HEA100, HEA200): Suitable for high-rise buildings bearing axial and vertical forces.
-
HEB Series (e.g., HEB100, HEB200): Ideal for small to medium-sized structures.
-
HEM Series (e.g., HEM100, HEM200): Lightweight design preferred for reduced material usage.
American Standards (ASTM/AISC): Simplified Naming, Multiple Strength Grades
Under ASTM A6/A6M, U.S. H-beams follow a "W+Size+Weight" format, such as W8×24, where "8" indicates the flange width (inches) and "24" represents weight per foot (pounds). Common strength grades include ASTM A36 and A572, with models like W8×18 and W10×33 widely used in industrial and civil construction.
British (BS) and Japanese (JIS) Standards: Detail-Oriented, Highly Adaptable
The British BS 4-1 standard covers HEA, HEB, and HEM series, with the HN series (e.g., HN200×100) emphasizing horizontal and vertical load-bearing capacity. Japan’s JIS G 3192 standard includes H-beams like H200×200 and H300×300, classified into SS400 (general Structural Steel) and SM490 (high tensile strength) grades, catering to both standard and heavy-duty construction.
German (DIN) and Australian (AS/NZS) Standards: Rigorous and Practical
Germany’s DIN 1025 standard (e.g., IPBL series) and Australia’s AS/NZS 1594 (e.g., 150UC23.4, 150UB18) emphasize product consistency and industrial applicability, serving both local and global markets.
Conclusion
While H-beam standards and models vary across regions, their shared goal is to ensure quality and meet engineering demands. Experts recommend selecting H-beams based on project specifications, environmental conditions, and budget constraints while adhering to local building codes. The rational use of H-beams continues to drive the global construction industry toward greater efficiency and standardization.
Email:manager@fsdsteel.com
Phone/Whatsapp:+86-18831507725