The difference, advantages and disadvantages and application scope of I-beam and H-beam
1. Sectional shape
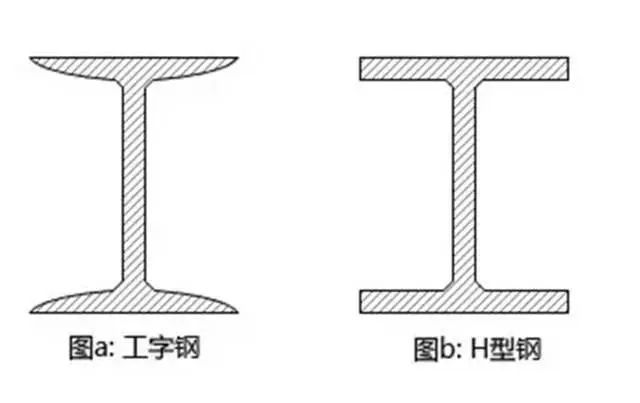
I-beams:
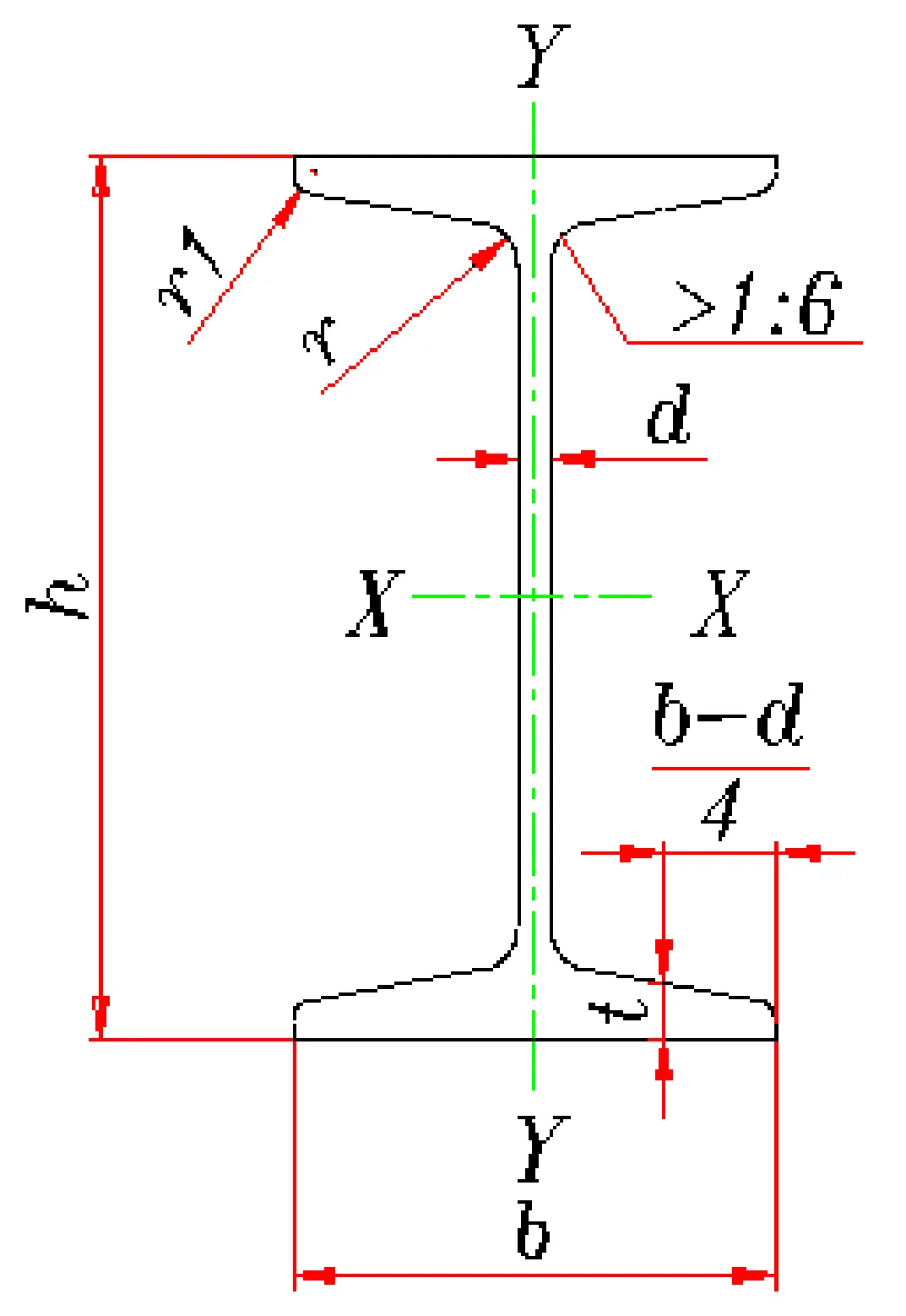
The wing edge is thick inside and thin outside, with a certain slope (usually 14%), and the cross-section is in the shape of an "I".
The belly plate is thick, the flange is narrow, and the edge is a curved transition.
H-beam:
The wing edges are equally thick and parallel, with a cross-section in an "H" shape and edges at right angles.
The flange is wide and thin, the thickness of the web plate is close to that of the flange, and the cross-section is more symmetrical.
2. Production process
I-beams: mainly formed by hot rolling once, with a simple process.
H-beam: divided into two processes: hot rolling and welding. High frequency welded H-beams are made by welding Steel Plates, while hot-rolled H-beams undergo multiple passes of rolling, making the process more complex.
3. Mechanical properties
I-Beam: It has good compressive performance, but weak bending resistance (narrow flange, uneven stress distribution).
H-beam: Excellent bending and torsion resistance (with wide and equally thick flanges and large sectional moments of inertia), high lateral stiffness.
4. Specification representation
I-beam: The model is represented by waist height (in centimeters), such as "16 #" indicating a waist height of 16cm.
H-beam: Mark height (H) x width (B) x web thickness (t1) x flange thickness (t2), such as H300 x 200 x 8 x 12.
5. Material utilization rate
I-beams have uneven material distribution due to the slope of the flange, while H-beams have a more reasonable cross-section, saving 10% -15% of steel.
2、 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| I-beam | 1. Low production cost and simple manufacturing process. 2. Strong compressive performance, suitable for columns. 3. Suitable for small to medium-span structures. | 1. Narrow flanges, weak bending resistance. 2. Low cross-sectional efficiency, more material waste. 3. Weak lateral stability, requiring additional support. |
| H-beam | 1. Optimized cross-section, strong bending and torsional resistance. 2. Wide flanges, good lateral stability. 3. High material utilization, lightweight structure. | 1. Complex production process, higher cost. 2. Hot-rolled H-beam specifications are limited by equipment. |
I-beam (I-steel) common specifications table
| 型号 | 高度 (h/mm) | 腿宽 (b/mm) | 腰厚 (d/mm) | 理论重量 (kg/m) | 截面面积 (cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10# | 100 | 68 | 4.5 | 11.261 | 14.3 |
| 12# | 120 | 74 | 5.0 | 13.987 | 17.8 |
| 14# | 140 | 80 | 5.5 | 16.890 | 21.5 |
| 16# | 160 | 88 | 6.0 | 20.513 | 26.1 |
| 18# | 180 | 94 | 6.5 | 24.143 | 30.6 |
| 20#a | 200 | 100 | 7.0 | 27.929 | 35.5 |
| 20#b | 200 | 102 | 9.0 | 31.069 | 39.5 |
Common specifications of H-beam (taking hot-rolled H-beam as an example)
Narrow flange H-beam (HN series)
| 型号 | 高度 (h/mm) | 腿宽 (b/mm) | 腹板厚 (t1/mm) | 翼缘厚 (t2/mm) | 理论重量 (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN150×75 | 150 | 75 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 14.3 |
| HN200×100 | 200 | 100 | 5.5 | 8.0 | 21.7 |
| HN250×125 | 250 | 125 | 6.0 | 9.0 | 29.7 |
| HN300×150 | 300 | 150 | 6.5 | 9.5 | 37.3 |
Wide flange H-beam (HW series)
| 型号 | 高度 (h/mm) | 腿宽 (b/mm) | 腹板厚 (t1/mm) | 翼缘厚 (t2/mm) | 理论重量 (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HW100×100 | 100 | 100 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 17.2 |
| HW150×150 | 150 | 150 | 7.0 | 10.0 | 31.9 |
| HW200×200 | 200 | 200 | 8.0 | 12.0 | 50.5 |
| HW300×300 | 300 | 300 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 94.5 |
3、 Scope of application
1. I-beam:
Applicable scenarios: Small and medium-sized building beams, mechanical equipment supports, temporary structural supports.
Typical applications: factory roof trusses, lightweight warehouse beams, transmission tower columns.
• Limitation: Not applicable to large-span or high lateral load scenarios.
2. H-beam:
Applicable scenarios: structures with large spans, heavy loads, and high stability requirements.
• Typical applications:
• High rise building frame (such as the core tube of Shanghai center Building).
Heavy duty factory building (steel structure factory main beam).
Bridge main beams (such as box girders for sea crossing bridges).
• Marine platforms, railway sleepers.
Advantage areas: earthquake zone buildings (excellent seismic performance), prefabricated buildings (standardized sections).
4、 Selection suggestions
Priority should be given to selecting I-beams: components with limited budget, small to medium spans (<12m), and mainly subjected to compression (such as columns).
Priority should be given to H-shaped steel: structures with large spans (>20m), high loads, and requiring bending/seismic resistance (such as high-rise building frame beams).
Special scenario: High frequency welded H-beams can be customized to non-standard sizes, suitable for irregular structures; Hot rolled H-beams are more suitable for standardized batch production.
5、 Development Trends
With the popularization of steel structure buildings, H-beams are gradually replacing traditional I-beams due to their efficient cross-sections, especially in the field of green buildings (reducing steel consumption). I-beams maintain cost advantages in temporary engineering and lightweight structures.