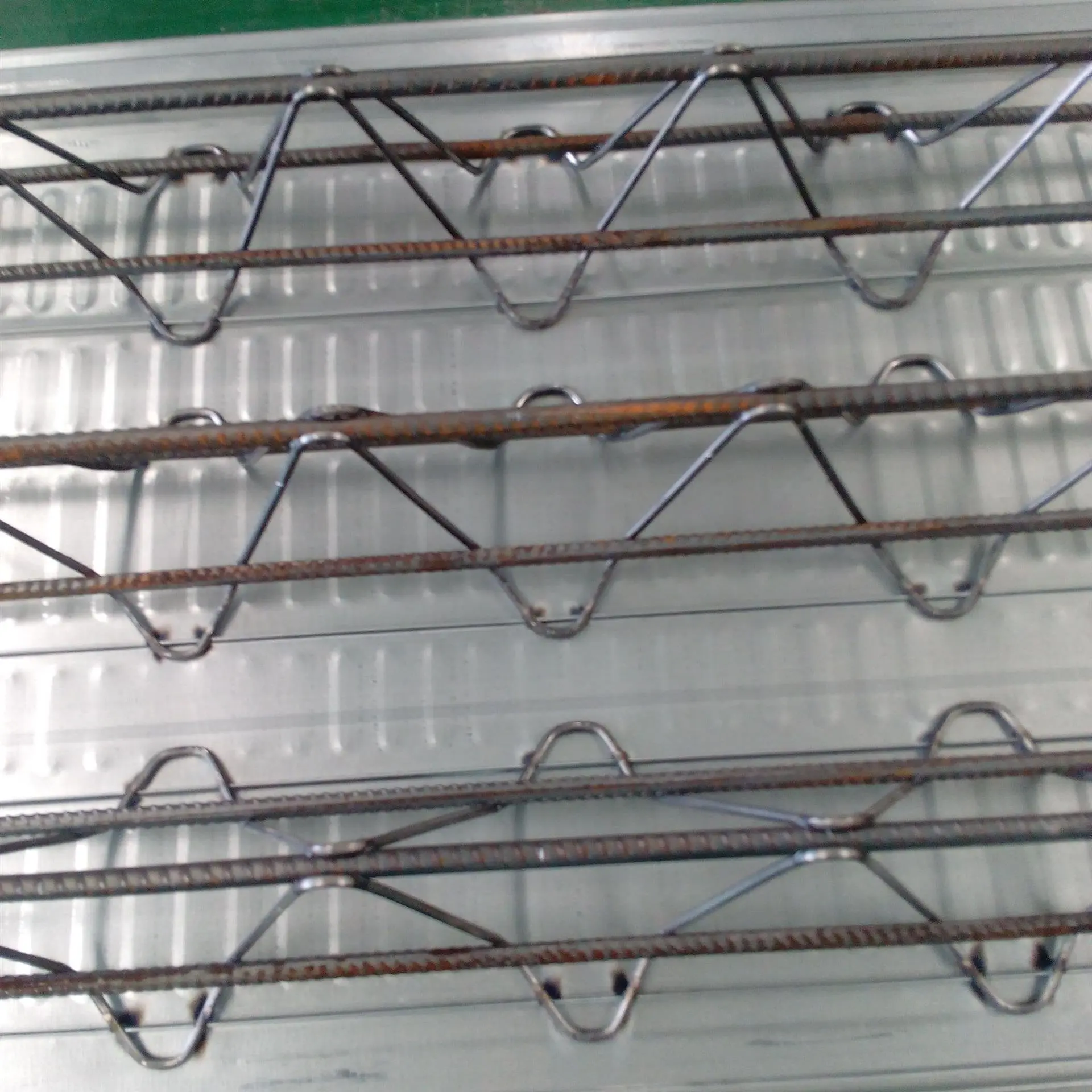
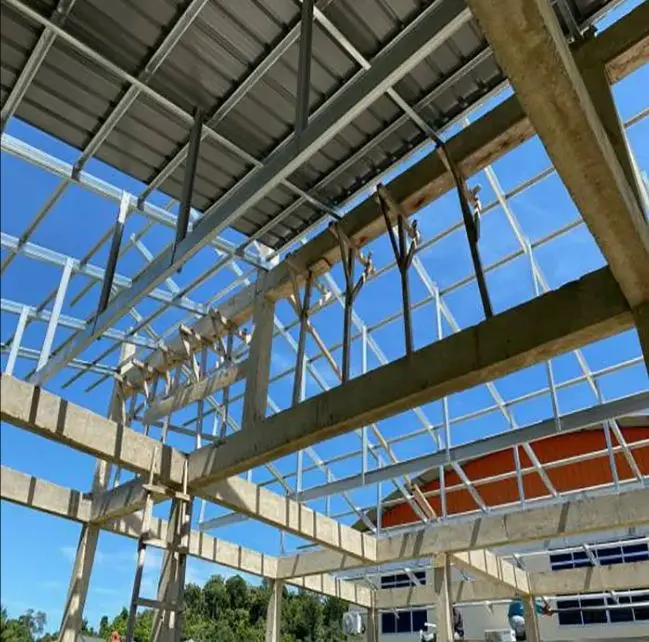
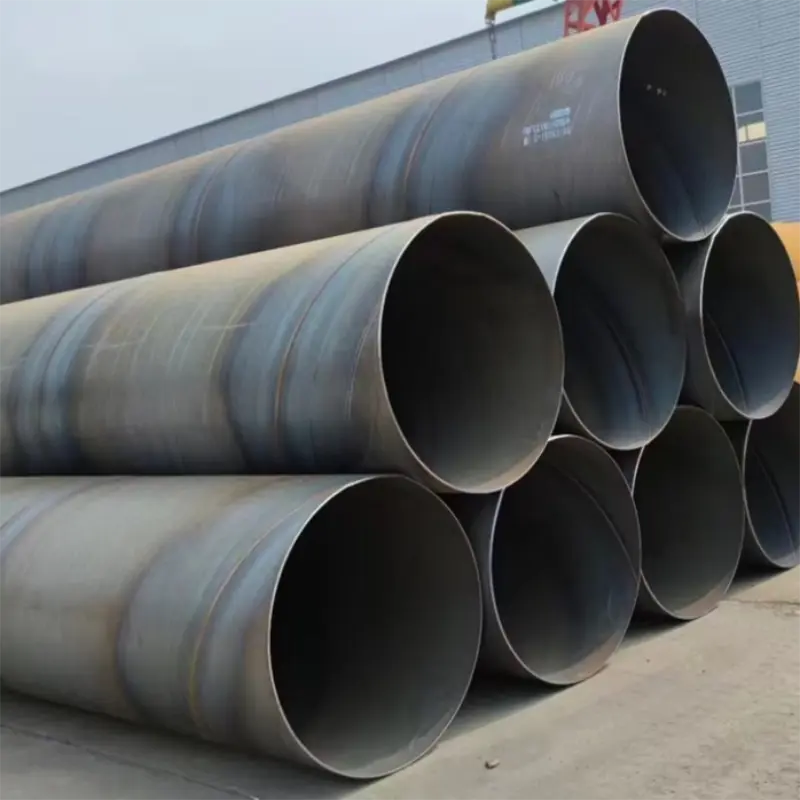
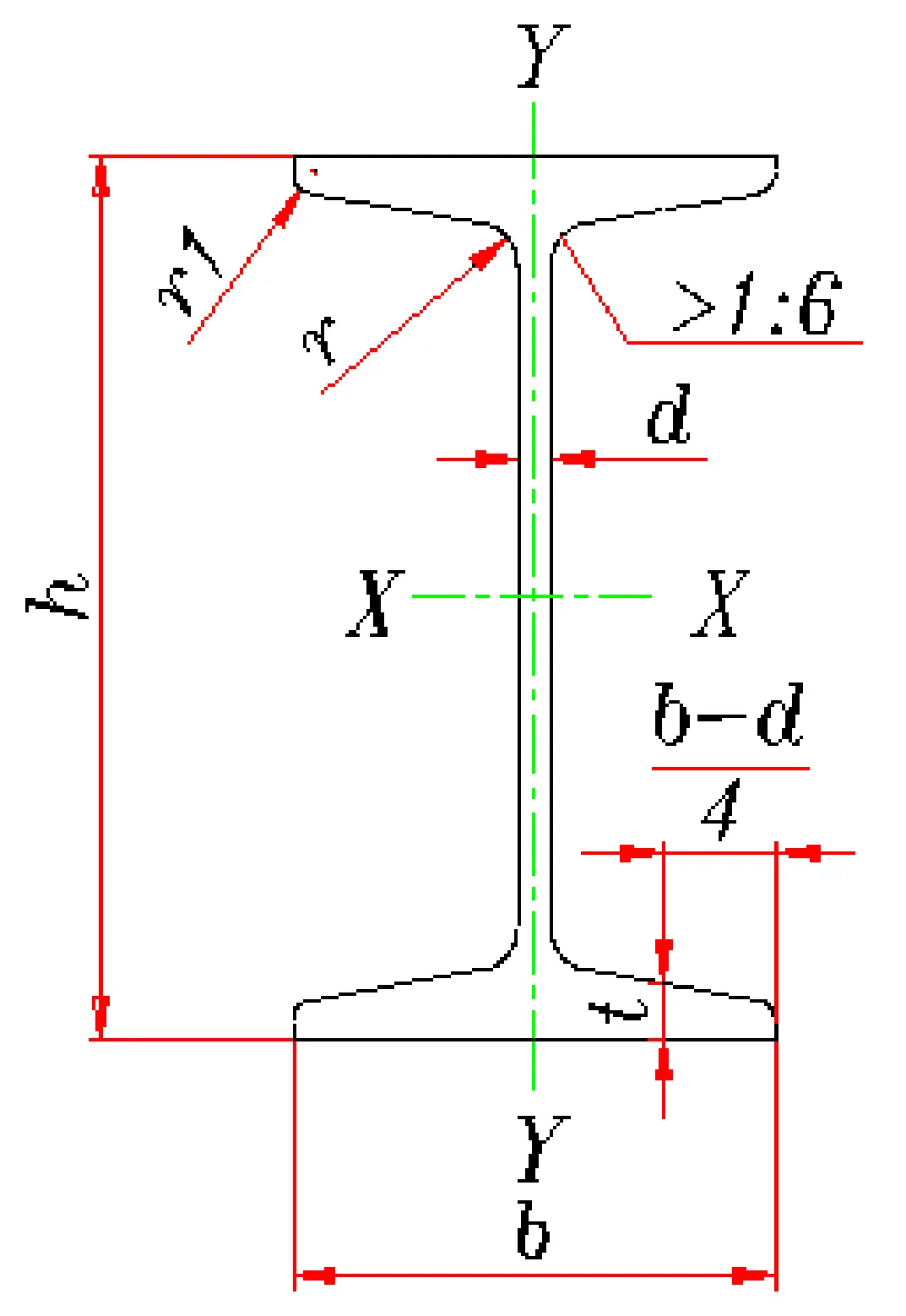
What is structural steel?
Structural steelis acategory of Steel used for making construction materials in a variety of shapes. Manystructural steel shapes take the form of an elongated Beam Havinga profile of a specific cross section. Structural steel shapes, sizes, chemicalcomposition, mechanical properties such as strengths, storage practices, etc.,are regulated by standards in most industrialized countries. Most structural steelshapes, such as I-beams, have high second moments of area, which means they arevery stiff in respect to their cross-sectional area and thus can support a highload without excessive sagging.
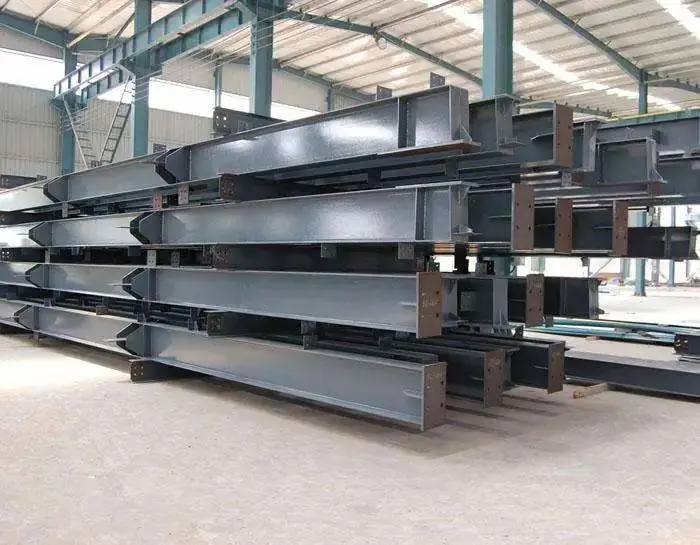

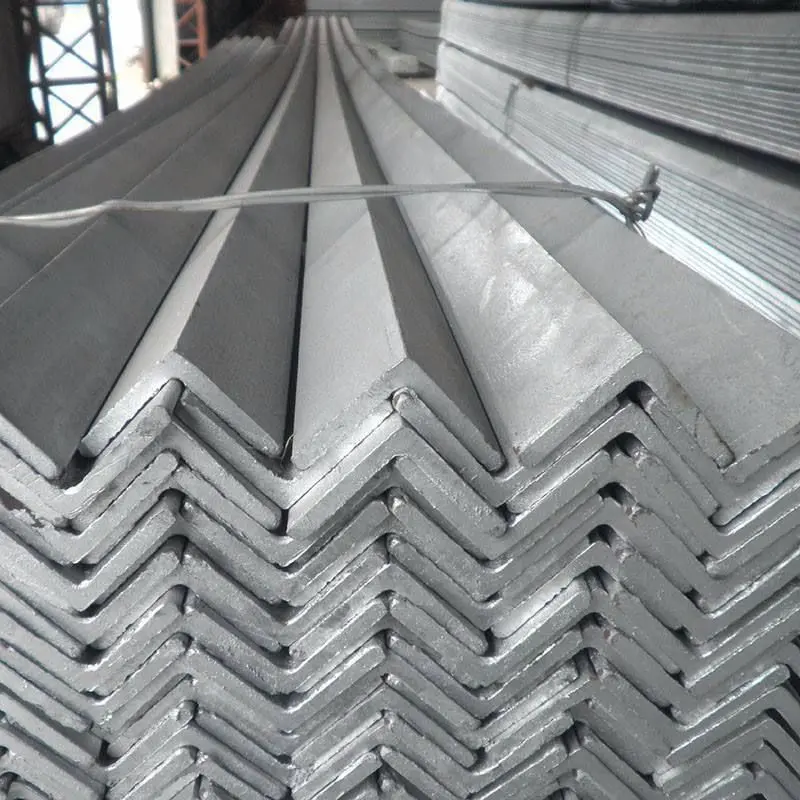
Structural steel is a vital category of steel used extensively in the construction industry to create a variety of shapes and forms. These shapes, often elongated beams with specific cross-sectional profiles, are engineered to provide exceptional strength and durability. Common examples include I-beams, H-beams, and angle irons, each designed to meet specific structural demands. The dimensions, chemical composition, mechanical properties (such as tensile and yield strength), and even storage practices for structural steel are rigorously regulated by standards in most industrialized countries, ensuring consistency and safety across projects.
One of the key advantages of structural steel is its high second moment of area, particularly in shapes like I-beams. This property makes these beams exceptionally stiff relative to their cross-sectional area, allowing them to support significant loads without excessive bending or sagging. This stiffness is crucial for maintaining the integrity of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure, especially in high-stress environments.
The versatility of structural steelextends beyond its mechanical properties. It can be fabricated into a wide range of shapes and sizes, making it suitable for diverse applications, from skyscrapers and industrial facilities to residential homes and temporary structures. Additionally, Structural Steel is often preferred for its sustainability, as it is recyclable and can be reused in future projects, reducing its environmental impact.
In recent years, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing have further enhanced the performance of structural steel. Innovations such as high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels and improved coating technologies have increased its resistance to corrosion and wear, extending the lifespan of structures and reducing maintenance costs.
As urbanization and infrastructure development continue to accelerate globally, the demand for structural steel is expected to grow. Its combination of strength, flexibility, and sustainability ensures that it will remain a cornerstone of modern construction for years to come.
Email:manager@fsdsteel.com