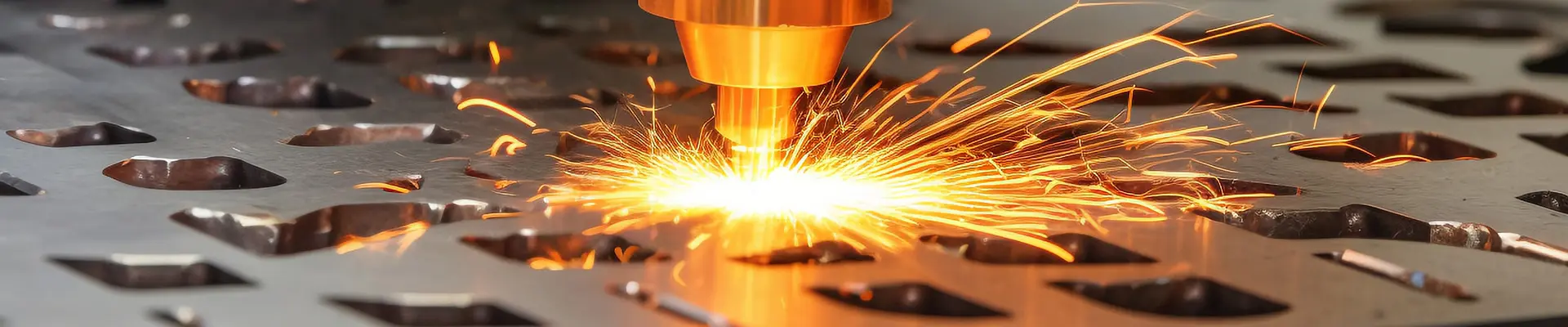
What is the difference between rebar and rebar
Threaded steelis a common name for hot-rolled ribbed Steel Bars, and there are two commonly used classification methods: one is to classify based on geometric shape, according to the different cross-sectional shapes of the ribs and the spacing between the ribs.


For example, in the British Standard (BS4449), threaded steelis divided into Type I and Type II. This classification method mainly reflects the gripping performance of threaded steel. Secondly, according to performance classification (grade), such as in the Chinese standard (GB1499.2-2018), threaded steel is divided into three grades based on strength grade (yield strength); In the Japanese Industrial Standard (JISG3112), Rebar is classified into five types based on its comprehensive performance. In addition, rebar can be classified according to its purpose, such as ordinary steel bars for reinforced concrete and heat-treated steel bars for reinforced concrete.
The standard for rebar in China is GB1499.2-2018, which is divided into ordinary hot-rolled steel bars and fine-grained hot-rolled steel bars. According to the standard definition, ordinary hot-rolled steel bars are steel bars delivered in a hot-rolled state. Its metallographic structure is mainly composed of ferrite and pearlite, and there must be no other structures that affect its performance. Fine grained hot-rolled steel bars refer to the fine grained steel bars formed through controlled rolling and controlled cooling processes during the hot rolling process. Its metallographic structure is mainly composed of ferrite and pearlite, and there should be no other structures that affect its performance. The grain size should not be coarser than grade 9.
The grade of ordinary hot-rolled ribbed steel bars consists of HRB, yield strength characteristic value, and seismic resistance mark (+E); The grade of fine grain hot-rolled ribbed steel bars consists of HRBF, yield strength characteristic value, and seismic symbol (+E) H. R, B, and E are the first letters of the four words' hot-rolled ',' ribbed ',' bars', and 'earthquake' respectively; F is the first letter of Fine in English. Ordinary hot-rolled steel bars are divided into five grades: HRB400, HRB500, HRB600, HRB400E, and HRB500E; The grades of fine-grained hot-rolled steel bars are divided into four grades: HRBF400, HRBF500, HRBF400E, and HRBF500E.
Threaded steel is widely used in civil engineering construction such as houses, bridges, and roads. From public facilities such as highways, railways, bridges, culverts, tunnels, flood control, dams, to foundations, beams, columns, walls, and slabs of buildings, threaded steel is an indispensable structural material.1. Different appearances. The outer surface of round steel is smooth; The outer surface of the threaded steel has spiral ribs.
2. Different production standards. In the current standard, round steel refers to HPB235 grade steel bars, and its production standard is "Hot Rolled Smooth Steel Bars for Reinforced Concrete" (GB13013); Threaded steel generally refers to HRB335 and HRB400 grade steel bars, and its production standard is "Hot rolled ribbed steel bars for reinforced concrete" (GB1499).
3. Different intensities. The design strength of round steel (HPB235) is 210MPa; The strength of threaded steel is higher than that of round steel, and the design strength of HRB335 is 300MPa; The design strength of HRB400 is 360MPa.
4. Different types of steel have different chemical compositions. Round steel (HPB235) belongs to carbon steel, and the steel grade is Q235; Threaded steel belongs to low-alloy steel, and HRB335 grade steel bars are 20MnSi (20 manganese silicon); HRB400 grade steel bars are made of materials such as 20MnSiV, 20MnSiNb, or 20MnTi.
Additional Information:
【1】 Precautions for threaded steel:
The quality of finished threaded steel bars varies with the metallurgical melting furnace and hot rolling batch process, and the furnace number and batch number are the basis for sampling inspection. Therefore, import and storage departments should pay attention to retaining the markings on the goods, and export enterprises and foreign trade departments should also distinguish batches and furnace numbers according to standard requirements and provide quality certificates.
Threaded steel is usually delivered naked and bundled. When storing, attention should be paid to moisture prevention. Corrosion will have a negative impact on the performance of threaded steel.
【2】 Production process of threaded steel:
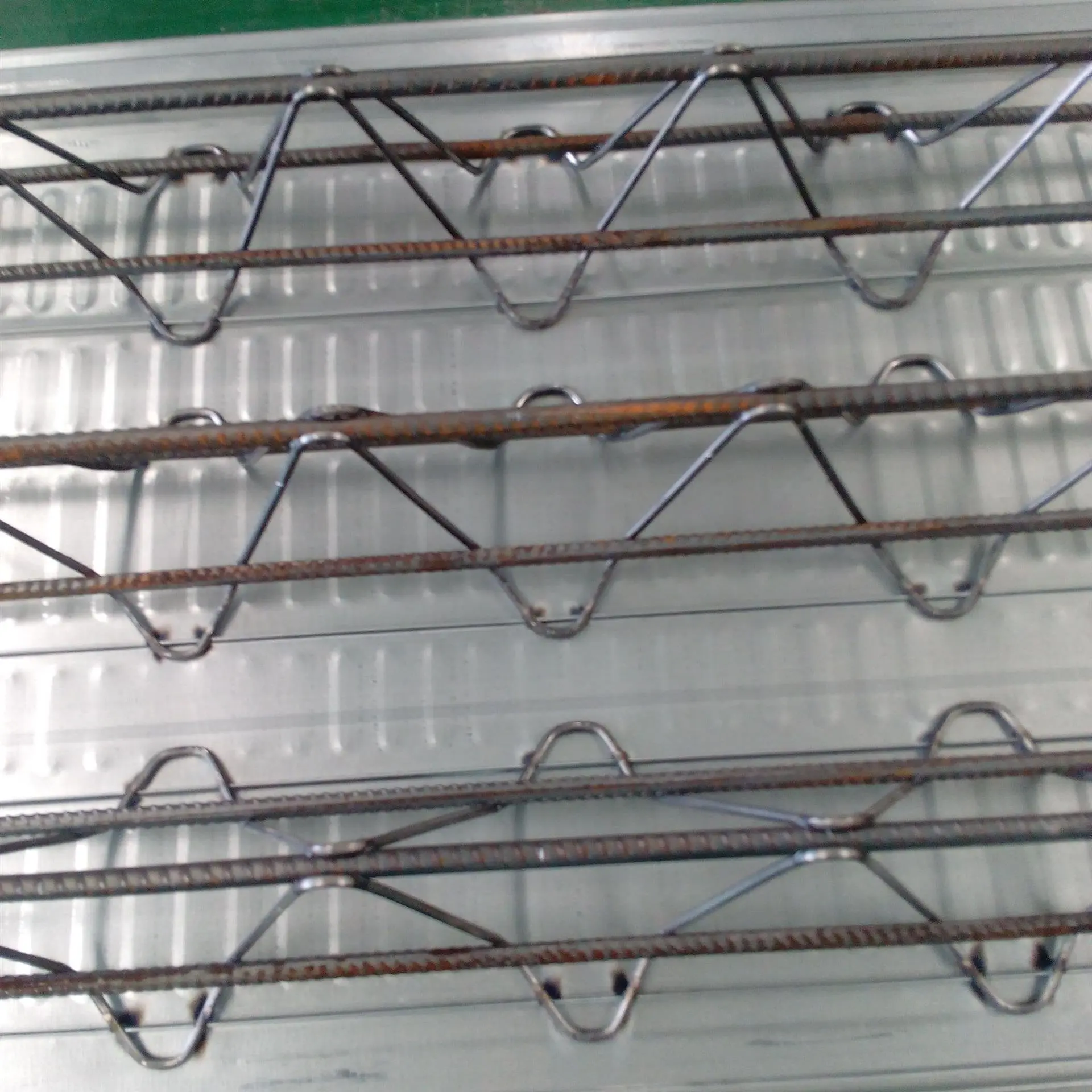
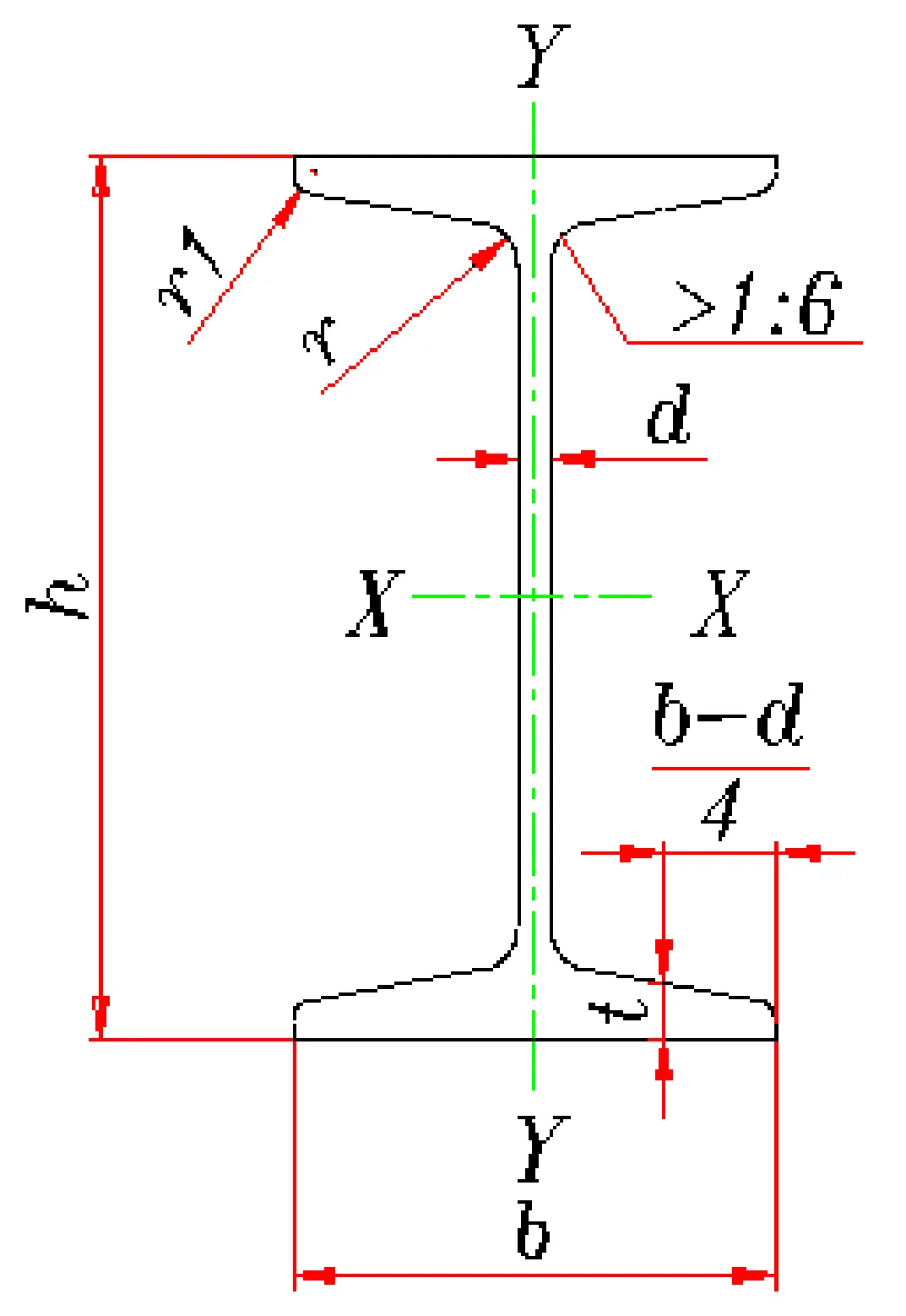
Threaded steel is a surface ribbed steel bar, also known as ribbed steel bar, usually with two longitudinal ribs and transverse ribs evenly distributed along the length direction. The shape of the transverse ribs is spiral, herringbone, and crescent. Expressed in millimeters of nominal diameter. The nominal diameter of ribbed steel bars is equivalent to the nominal diameter of round steel bars with equal cross-sections. The nominal diameter of steel bars is 8-50 millimeters, and recommended diameters are 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, 32, and 40 millimeters.
Ribbed steel bars mainly bear tensile stress in concrete. Ribbed steel bars, due to the action of ribs, have a greater bonding ability with concrete and can better withstand external forces. Ribbed steel bars are widely used in various building structures, especially large, heavy, lightweight thin-walled and high-rise building structures.
Threaded steel is produced by small rolling mills, which are mainly divided into continuous, semi continuous, and transverse types. Most of the newly built and in use fully continuous small rolling mills in the world. The popular steel bar rolling mills include the universal high-speed rolling steel bar rolling mill and the 4-section high-yield steel bar rolling mill.
The billet used for continuous small rolling mills is generally continuous casting small billets, with a side length of 130-160mm and a length of about 6-12 meters. The billet weighs 1.5-3 tons per unit. The rolling lines are mostly arranged in a flat interchange layout, achieving non twisting rolling throughout the entire line. There are 18, 20, 22, and 24 small rolling mills available according to different specifications of raw materials and finished product sizes, with 18 being the mainstream.
Bar rolling often adopts new processes such as step heating furnace, high-pressure water descaling, low-temperature rolling, and headless rolling. Coarse rolling and medium rolling are developing towards adapting to large billets and improving rolling accuracy, while precision rolling machines mainly focus on improving accuracy and speed (up to 18m/s). The product specifications are generally ф 10-40mm, but there are also ф 6-32mm or ф 12-50mm. The steel grades produced are low, medium, high carbon steel and low-alloy steel that are in high demand in the market; The maximum rolling speed is 18m/s. The production process is as follows:
Step heating furnace → roughing mill → intermediate rolling mill → finishing mill → water cooling device → cold bed → cold shear → automatic counting device → baler → unloading platform